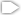
Disk of Debris Around Red Dwarf Star AU Microscopii

stsci_2004-33b December 9th, 2004
Credit: NASA, ESA, J.E. Krist (STScI/JPL); D.R. Ardila (JHU); D.A. Golimowski (JHU); M. Clampin (NASA/Goddard); H.C. Ford (JHU); G.D. Illingworth (UCO-Lick); G.F. Hartig (STScI) and the ACS Science Team
A visible-light image of a debris disk around the red dwarf star AU Microscopii. Planets may be forming, or might already exist, within it. The disk glows in starlight reflected by tiny grains of dust created by the collisions of asteroids and comets. Because it is composed of the pulverized remnants of these objects, it is called a "debris disk." More than 40 billion miles across, it appears like a spindle of light because we view it nearly edge on (like looking at a dinner plate along its side). The star is about 12 million years old and is only 32 light-years from Earth. This makes its disk the closest yet seen in reflected starlight. It is also the first disk imaged around an M-type red dwarf, the most common type of star in the stellar neighborhood around the Sun. The Hubble Space Telescope images, taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) reveal that the disk has been cleared of dust within about a billion miles of the star (first indicated from infrared-light measurements). The ACS images confirm that the disk is warped and has small variations in dust density that, along with the central clearing, may be caused by the tugging of an unseen companion, perhaps a large planet. ACS shows that this is the only debris disk known that appears bluer than the star it surrounds. This may indicate that there are more small grains of dust, compared to large ones, than has been seen before in other such disks. Smaller grains scatter blue light better than red. The surplus of small grains may be due to the fact that the star is not bright enough to blow away these tiny particles. In brighter, hotter stars, the pressure from radiation can actually push small dust grains out of the disk and far out into space.
Provider: Space Telescope Science Institute
Image Source: https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2004/news-2004-33
Curator: STScI, Baltimore, MD, USA
Image Use Policy: http://hubblesite.org/copyright/

- ID
- 2004-33b
- Subject Category
- B.3.3.1 B.3.7.2.3
- Subject Name
- AU Mic, GJ 803, HD197481
- Credits
- NASA, ESA, J.E. Krist (STScI/JPL); D.R. Ardila (JHU); D.A. Golimowski (JHU); M. Clampin (NASA/Goddard); H.C. Ford (JHU); G.D. Illingworth (UCO-Lick); G.F. Hartig (STScI) and the ACS Science Team
- Release Date
- 2004-12-09T00:00:00
- Lightyears
- 33
- Redshift
- 33
- Reference Url
- https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2004/news-2004-33
- Type
- Observation
- Image Quality
- Good
- Distance Notes
- Distance in lightyears
- Facility
- Hubble
- Instrument
- ACS/HCR
- Color Assignment
- Band
- Optical
- Bandpass
- V
- Central Wavelength
- 606
- Start Time
- Integration Time
- Dataset ID
- Notes
- Coordinate Frame
- ICRS
- Equinox
- Reference Value
- 34.77708333, 16.54830278
- Reference Dimension
- Reference Pixel
- Scale
- Rotation
- Coordinate System Projection:
- Quality
- Position
- FITS Header
- Notes
- Creator (Curator)
- STScI
- URL
- http://hubblesite.org
- Name
- Space Telescope Science Institute Office of Public Outreach
- outreach@stsci.edu
- Telephone
- 410-338-4444
- Address
- 3700 San Martin Drive
- City
- Baltimore
- State/Province
- MD
- Postal Code
- 21218
- Country
- USA
- Rights
- http://hubblesite.org/copyright/
- Publisher
- STScI
- Publisher ID
- stsci
- Resource ID
- STSCI-H-p0433b-f-800x600.tif
- Resource URL
- https://mast.stsci.edu/api/latest/Download/file?uri=mast:OPO/product/STSCI-H-p0433b-f-800x600.tif
- Related Resources
- http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2004/33
- Metadata Date
- 2022-07-06T00:00:00
- Metadata Version
- 1.2
Detailed color mapping information coming soon...