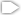
Nearby Dust Clouds in the Milky Way

stsci_2006-13a April 4th, 2006
Credit: NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: P. McCullough (STScI)
The yearly ritual of spring cleaning clears a house of dust as well as dust "bunnies," those pesky dust balls that frolic under beds and behind furniture. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has photographed similar dense knots of dust and gas in our Milky Way Galaxy. This cosmic dust, however, is not a nuisance. It is a concentration of elements that are responsible for the formation of stars in our galaxy and throughout the universe. These opaque, dark knots of gas and dust are called "Bok globules," and they are absorbing light in the center of the nearby emission nebula and star-forming region, NGC 281. The globules are named after astronomer Bart Bok, who proposed their existence in the 1940's. Bok hypothesized that giant molecular clouds, on the order of hundreds of light-years in size, can become perturbed and form small pockets where the dust and gas are highly concentrated. These small pockets become gravitationally bound and accumulate dust and gas from the surrounding area. If they can capture enough mass, they have the potential of creating stars in their cores; however, not all Bok globules will form stars. Some will dissipate before they can collapse to form stars. That may be what's happening to the globules seen here in NGC 281. Near the globules are bright blue stars, members of the young open cluster IC 1590. The cluster is made up of a few hundred stars. The cluster's core, off the image towards the top, is a tight grouping of extremely hot, massive stars with an immense stellar wind. The stars emit visible and ultraviolet light that energizes the surrounding hydrogen gas in NGC 281. This gas then becomes super heated in a process called ionization, and it glows pink in the image. The Bok globules in NGC 281 are located very close to the center of the IC 1590 cluster. The exquisite resolution of these Hubble observations shows the jagged structure of the dust clouds as if they are being stripped apart from the outside. The heavy fracturing of the globules may appear beautifully serene but is in fact evident of the harsh, violent environment created by the nearby massive stars. The Bok globules in NGC 281 are visually striking nonetheless. They are silhouetted against the luminous pink hydrogen gas of the emission nebula, creating a stark visual contrast. The dust knots are opaque in visual light. Conversely, the nebulous gas surrounding the globules is transparent and allows light from background stars and even background galaxies to shine through. These images were taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in October 2005. The hydrogen-emission image that clearly shows the outline of the dark globules was combined with images taken in red, blue, and green light in order to help establish the true color of the stars in the field. NGC 281 is located nearly 9,500 light-years away in the direction of the constellation Cassiopeia.
Provider: Space Telescope Science Institute
Image Source: https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2006/news-2006-13
Curator: STScI, Baltimore, MD, USA
Image Use Policy: http://hubblesite.org/copyright/

- ID
- 2006-13a
- Subject Category
- B.4.2.1 B.4.2.3
- Subject Name
- Bok globules in NGC 281
- Credits
- NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: P. McCullough (STScI)
- Release Date
- 2006-04-04T00:00:00
- Lightyears
- 9,500
- Redshift
- 9,500
- Reference Url
- https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2006/news-2006-13
- Type
- Observation
- Image Quality
- Good
- Distance Notes
- 9,500 light-years (2.9 kiloparsecs)
- Facility
- Hubble, Hubble, Hubble, Hubble
- Instrument
- ACS, ACS, ACS, ACS
- Color Assignment
- Band
- Optical, Optical, Optical, Optical
- Bandpass
- B, V, Halpha, I
- Central Wavelength
- 435, 555, 658, 814
- Start Time
- 2005-10-31T00:00:00, 2005-10-31T00:00:00, 2005-10-31T00:00:00, 2005-10-31T00:00:00
- Integration Time
- Dataset ID
- Notes
- 3
- Coordinate Frame
- ICRS
- Equinox
- 2000.0
- Reference Value
- 13.26608080000, 56.64178050000
- Reference Dimension
- 2873.00, 3885.00
- Reference Pixel
- 1643.45711276803, 2006.52880847595
- Scale
- -0.00001385333, 0.00001385333
- Rotation
- 113.00287548768
- Coordinate System Projection:
- TAN
- Quality
- Full
- FITS Header
- Notes
- World Coordinate System resolved using PinpointWCS 0.9.2 revision 218+ by the Chandra X-ray Center
- Creator (Curator)
- STScI
- URL
- http://hubblesite.org
- Name
- Space Telescope Science Institute Office of Public Outreach
- outreach@stsci.edu
- Telephone
- 410-338-4444
- Address
- 3700 San Martin Drive
- City
- Baltimore
- State/Province
- MD
- Postal Code
- 21218
- Country
- USA
- Rights
- http://hubblesite.org/copyright/
- Publisher
- STScI
- Publisher ID
- stsci
- Resource ID
- STSCI-H-p0613a-f-2873x3885.tif
- Resource URL
- https://mast.stsci.edu/api/latest/Download/file?uri=mast:OPO/product/STSCI-H-p0613a-f-2873x3885.tif
- Related Resources
- http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2006/13
- Metadata Date
- 2022-07-06T00:00:00
- Metadata Version
- 1.2
Detailed color mapping information coming soon...