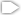
Jupiter's Great Red Spot

stsci_2020-21a May 7th, 2020
Credit: NASA, ESA, and M.H. Wong (UC Berkeley) and team
These images of Jupiter's Great Red Spot were made using data collected by the Hubble Space Telescope and the Gemini Observatory on April 1, 2018. By combining observations captured at almost the same time from the two different observatories, astronomers were able to determine that dark features on the Great Red Spot are holes in the clouds rather than masses of dark material. Upper left (wide view) and lower left (detail): The Hubble image of sunlight (visible wavelengths) reflecting off clouds in Jupiter’s atmosphere shows dark features within the Great Red Spot. Upper right: A thermal infrared image of the same area from Gemini shows heat emitted as infrared energy. Cool overlying clouds appear as dark regions, but clearings in the clouds allow bright infrared emission to escape from warmer layers below. Lower middle: An ultraviolet image from Hubble shows sunlight scattered back from the hazes over the Great Red Spot. The Great Red Spot appears red in visible light because these hazes absorb blue wavelengths. The Hubble data show that the hazes continue to absorb even at shorter ultraviolet wavelengths. Lower right: A multiwavelength composite of Hubble and Gemini data shows visible light in blue and thermal infrared in red. The combined observations show that areas that are bright in infrared are clearings or places where there is less cloud cover blocking heat from the interior.
The Hubble and Gemini observations were made to provide a wide-view context for Juno’s 12th pass (Perijove 12).
Provider: Space Telescope Science Institute
Image Source: https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2020/news-2020-21
Curator: STScI, Baltimore, MD, USA
Image Use Policy: http://hubblesite.org/copyright/

- ID
- 2020-21a
- Subject Category
- A.1.1.2
- Subject Name
- Jupiter
- Credits
- NASA, ESA, and M.H. Wong (UC Berkeley) and team
- Release Date
- 2020-05-07T00:00:00
- Lightyears
- Redshift
- Reference Url
- https://hubblesite.org/contents/news-releases/2020/news-2020-21
- Type
- Collage
- Image Quality
- Good
- Distance Notes
- Facility
- Hubble, Gemini
- Instrument
- WFC3/UVIS, NIRI
- Color Assignment
- Band
- Bandpass
- Central Wavelength
- Start Time
- Integration Time
- Dataset ID
- Notes
- Coordinate Frame
- ICRS
- Equinox
- Reference Value
- 289.2286250, -22.6642639
- Reference Dimension
- Reference Pixel
- Scale
- Rotation
- Coordinate System Projection:
- Quality
- Position
- FITS Header
- Notes
- Creator (Curator)
- STScI
- URL
- http://hubblesite.org
- Name
- Space Telescope Science Institute Office of Public Outreach
- outreach@stsci.edu
- Telephone
- 410-338-4444
- Address
- 3700 San Martin Drive
- City
- Baltimore
- State/Province
- MD
- Postal Code
- 21218
- Country
- USA
- Rights
- http://hubblesite.org/copyright/
- Publisher
- STScI
- Publisher ID
- stsci
- Resource ID
- STSCI-H-p2021a-f-2481x1462.tif
- Resource URL
- https://mast.stsci.edu/api/latest/Download/file?uri=mast:OPO/product/STSCI-H-p2021a-f-2481x1462.tif
- Related Resources
- Metadata Date
- 2021-12-14T13:45:57-05:00
- Metadata Version
- 1.2
Detailed color mapping information coming soon...